What exactly is the magic behind those eerily realistic videos you’ve seen online? The short answer is: AI, specifically a type called deep learning. But it’s a bit more complicated than that, and we are going to unpack exactly how these sometimes-convincing, often-troubling synthetic media pieces are made.
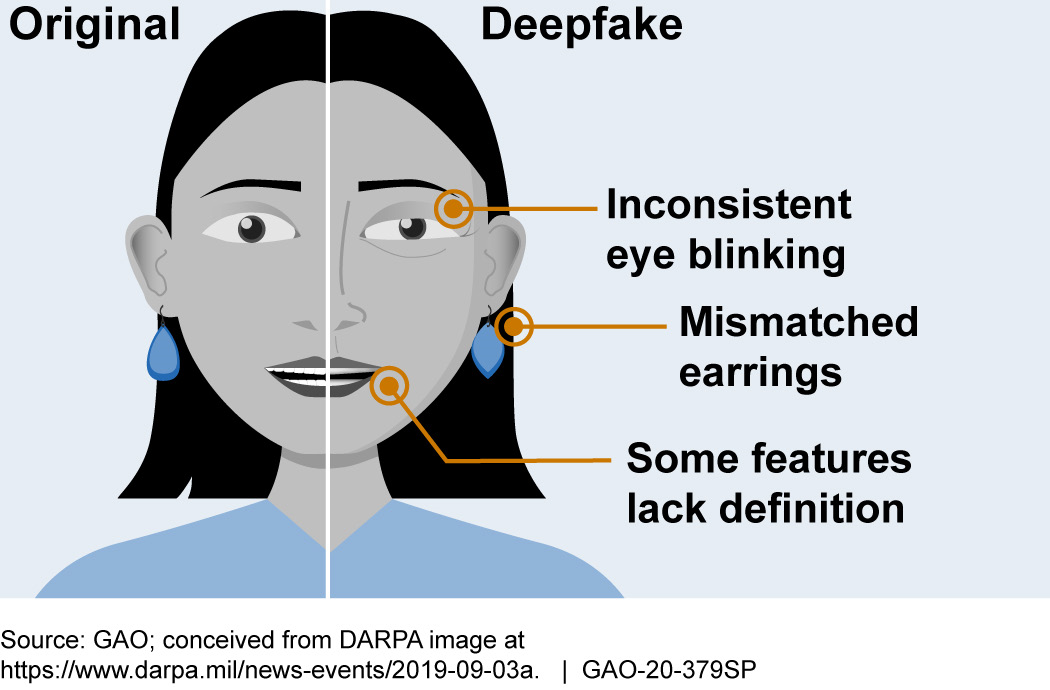
Image Source: www.gao.gov
The Genesis of a Fake: Deep Learning’s Role
At the heart of AI deepfake generation lies deep learning, a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks. Think of a neural network like a complex web of interconnected “neurons,” inspired by the structure of the human brain. These networks learn by analyzing tons of data, and the more data you feed them, the better they become at recognizing patterns and making predictions.
Deep learning deepfakes rely on the ability of these networks to understand and manipulate images and video. Specifically, the process of creating a deepfake usually involves two main neural networks working together. It’s like two artists, one trying to create a forgery, and the other trying to spot the fake.
The Two Artists: Understanding the Generative Adversarial Network
This duo of networks is known as a Generative Adversarial Network, or GAN. We’ll break down what each side does:
- The Generator: This network’s job is to create a fake image or video that looks as close to real as possible. It starts with random noise and gradually learns to generate images that match the training data.
- The Discriminator: This network’s role is to distinguish between real images and fake images produced by the Generator. It acts as a critic, telling the Generator what’s good and what needs improving.
The Generator and Discriminator are locked in a constant battle. The Generator creates a fake, and the Discriminator tries to catch it. If the Discriminator fails, the Generator is doing a good job. Through this constant back-and-forth, both networks improve, and the Generator becomes increasingly skilled at making near-perfect fakes. This cycle is the core of generative adversarial networks deepfakes and leads to the increasingly sophisticated results we see today.
Feeding the Beast: The Data Deepfakes Need
How do these networks learn to mimic a specific person’s face? It all comes down to data, specifically the huge amount of images and videos needed for training. Imagine trying to learn a new language just by hearing a few random words. You wouldn’t get very far. It’s the same for deep learning, networks need a lot of information to accurately understand and replicate features.
- Face Data Collection: Creators of deepfakes typically gather a large collection of photos and videos of the target individual. The more angles, expressions, and lighting conditions available, the better the results. This can include anything from social media posts to public videos.
- Pre-Processing: This data then undergoes pre-processing, a stage where images might be cropped, resized, or have their quality standardized. This ensures the training process is effective.
The more high quality, varied data a deepfake creator can gather, the more convincing the result is likely to be. This is often why public figures are particularly vulnerable; there is ample footage of them readily available online. This highlights the potential ethical concerns surrounding data collection and privacy, especially in the context of AI generated content. Based on extensive knowledge of various ethical aspects of AI, the need for responsible data collection cannot be stressed enough.
The Core Techniques: How The Magic Really Happens
While GANs are the overall architecture, here are some of the specific techniques used to achieve realistic deepfake video synthesis:
Facial Manipulation AI: Mapping the Face
A primary step in creating convincing deepfakes is accurate facial mapping. Here’s how it works:
- Facial Landmarks: AI algorithms identify key facial features or “landmarks”, such as the corners of the eyes, the tip of the nose, and the edges of the mouth.
- Spatial Mapping: These landmarks create a spatial map of the face. The deep learning model then uses this map to understand how the different facial features relate to each other.
- Face Swapping: Once the mapping is complete, the algorithm can swap the mapped features of one person onto another. This forms the basis of the “face-swapping” often seen in deepfakes.
Encoding and Decoding: Translating Faces
Encoding and decoding are crucial to manipulating the face, and are achieved with autoencoders, which are a specialized type of neural network.
- The Encoder: This part of the network takes an image of a face and compresses it into a simplified code. Think of it as turning a detailed description of a face into a shorthand version.
- The Decoder: Then, another part of the network takes that shorthand version and reconstructs the original face from it. This is the decoding process.
- Manipulation Through Code: By tweaking or swapping the code between the encoding and decoding process, the AI can then modify the face in various ways, effectively swapping features between people.
Lip Syncing and Audio: A Symphony of Deception
To enhance the realism, many deepfakes now include manipulated audio and lip-sync.
- Speech Synthesis: AI models can generate speech that sounds like the target person, using samples of their real voice. The AI can then use this voice to create new words, sentences, or entire speeches that the target person has never actually said.
- Lip Movement Matching: This new audio then goes through another AI process where they can manipulate the lips in the video to match the generated speech. AI models can analyze and then mimic lip movements, so they match the fabricated audio. This is key in making deepfakes appear more convincing.
The Algorithm Under The Hood: Key Aspects
Here is a summary of the deepfake algorithms that play an important role in the process.
| Algorithm | Function |
|---|---|
| Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) | The overarching structure that involves a generator that creates the fake content and discriminator that evaluates the realness. |
| Autoencoders | Employed for encoding and decoding image representations, allowing for manipulation and reconstruction of faces. |
| Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) | Applied for image processing tasks such as feature extraction and facial landmark detection. |
| Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) | Used for tasks involving sequences like audio synthesis and lip syncing. |
| Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) | An alternative to Autoencoders that can produce more varied and natural outputs, often used in higher quality deepfakes. |
The Road to Realism: Constant Evolution
How are deepfakes made has evolved at a rapid pace. In just a few years, we have seen them go from simple face swaps to sophisticated video and audio manipulations. Deepfakes are rapidly evolving, and future advancements might make them more difficult to detect. With experience in working with various image processing techniques, the need to stay updated is key to understanding future trends in this area.
- Increased Resolution: Early deepfakes were often low quality and blurry. Advances in techniques and computation power means higher resolution deepfakes are now common.
- Improved Lip Sync and Audio: Early deepfake audio and lip syncing felt robotic. With better AI models, the synchronization of audio and visuals has gotten much more seamless.
- More Sophisticated Manipulation: AI models are becoming more sophisticated at handling subtle facial nuances and changes in expression, making deepfakes much more realistic.
Beyond the Visuals: Other Synthetic Media
While deepfakes are mostly associated with video, it’s important to consider the broader concept of synthetic media creation:
- Text Synthesis: AI can now generate very convincing text, from fake news articles to fabricated social media posts.
- Audio Synthesis: As mentioned before, AI can create human-sounding voices that can be used in any context.
- Image Synthesis: AI models are also adept at creating realistic images of people, places, and things that do not exist in real life.
These methods, and their use in synthetic media creation, are something to be very aware of as the technology advances.
Detecting The Fakes: Our Role In Reality’s Defense
As deepfakes become more convincing, the ability to detect them is critical. Here are some techniques being used and researched:
- Visual Artifact Analysis: Looking for subtle inconsistencies in the video itself, such as unrealistic lighting, unusual blurs, or facial glitches.
- Facial Movement Analysis: AI algorithms are being developed to identify the unnatural micro-movements or distortions in a fake face.
- Metadata Analysis: Analyzing the origin and context of a video or images to verify whether it is real.
- AI-powered Detection Tools: AI models are also being developed that can distinguish between real and fake videos.
The Ethical Quandary: What It All Means
The rise of AI-generated content brings with it a range of ethical concerns:
- Misinformation and Propaganda: Deepfakes can easily be used to spread false information, damage reputations, and manipulate public opinion.
- Non-Consensual Use: There is a potential for the creation and use of deepfakes without a person’s consent, leading to severe emotional distress and reputational harm.
- Erosion of Trust: As AI-generated content becomes increasingly convincing, the ability to trust information from sources will erode.
- Political Manipulation: Deepfakes can be easily weaponized for political smear campaigns and election tampering.
The implications of deepfake technology explained are profound, and it is important to understand both the technical details as well as the potential consequences. This is not just a technological issue, it is very much a societal and ethical issue.
FAQ: Digging Deeper Into Deepfakes
Q: Can I create a deepfake myself?
A: Yes, with the right tools and some technical know-how, anyone can create deepfakes. There are accessible deepfake software tools and open-source libraries available online, although the best results still require some expertise and computational resources.
Q: How can I tell if a video is a deepfake?
A: There are some techniques to try, although not always foolproof: Look for unnatural blinking patterns, inconsistent lighting, or blurry areas. Pay attention to any strange movements of the face, especially around the lips. However, the best way is to be skeptical of any videos that are very shocking or seem unusual. Use reputable news outlets to find whether or not a video has been debunked as a deepfake.
Q: Who is most vulnerable to deepfakes?
A: Anyone with a substantial online presence can become a target for deepfakes, but public figures are especially vulnerable. Because there is a lot of image and video data of them readily available, this makes it easier for deepfake creators to get the data that they need.
Q: Are there laws against creating deepfakes?
A: The legal status of deepfakes is still evolving. Many countries and states are now beginning to implement laws and regulations regarding the creation and distribution of deepfakes, especially those that are used for malicious or deceptive purposes.
Q: What is being done to combat the misuse of deepfakes?
A: There are a range of measures being put into place to fight deepfakes, including the development of deepfake detection technologies, regulations against malicious use, and public education initiatives.
Q: What’s the difference between a deepfake and other types of media manipulation?
A: Deepfakes use AI and deep learning to create highly realistic fake content. While other methods of media manipulation, such as Photoshop or simple video editing, have existed for many years, deepfakes stand out because they are often very difficult to detect, especially as the technology improves.
The journey into understanding the world of deepfakes is certainly a complex one. As we have seen, deepfakes are a product of amazing advancements in AI, but the responsible use of this powerful technology is something we all need to think about.
I’m Rejaul Karim, an SEO and CRM expert with a passion for helping small businesses grow online. I specialize in boosting search engine rankings and streamlining customer relationship management to make your business run smoothly. Whether it's improving your online visibility or finding better ways to connect with your clients, I'm here to provide simple, effective solutions tailored to your needs. Let's take your business to the next level!

