The question “When was AI created?” doesn’t have a single, straightforward answer. It’s more like peeling back the layers of an onion, revealing a fascinating history of ai development filled with brilliant ideas and gradual progress. The seeds of artificial intelligence were sown long before the computer age, but the actual field took root in the mid-20th century. So, while we might not pinpoint an exact birth date, we can say the formal journey of AI ai origins began around the 1950s.
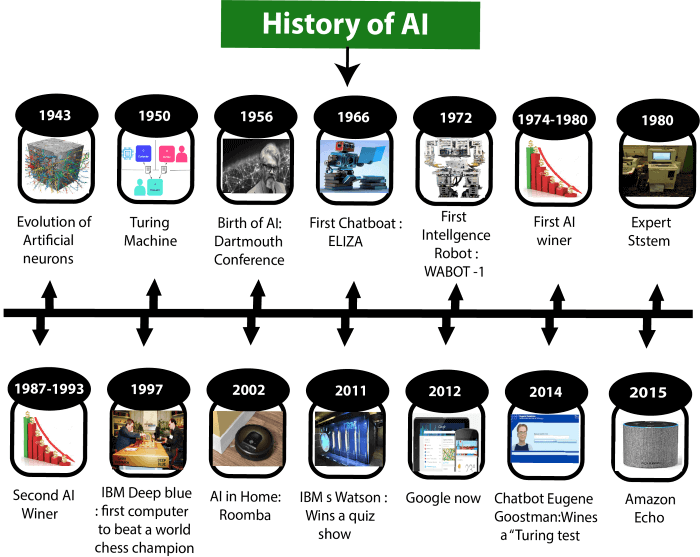
Image Source: miro.medium.com
Imagining Machines That Think: Pre-Computer Visions
Long before the first computer existed, thinkers were already toying with the idea of machines that could mimic human thought. These early imaginings laid a crucial foundation for the artificial intelligence timeline.
- Ancient myths and legends: Stories of automatons, like Talos, a giant bronze robot in Greek mythology, hinted at humanity’s long fascination with creating artificial beings.
- 17th-19th Centuries: Philosophers and mathematicians like René Descartes, Charles Babbage, and Ada Lovelace began exploring the possibility of machines performing complex tasks, even those seemingly requiring intelligence. Babbage, for instance, designed the “Analytical Engine” – a mechanical general-purpose computer. Ada Lovelace is often considered the first computer programmer, envisioning the potential of such machines to do much more than mere calculations.
- Early 20th Century: Writers like Karel Čapek, who coined the term “robot” in his 1920 play “Rossum’s Universal Robots,” helped shape popular ideas about artificial beings, often highlighting the complex ethical questions.
These weren’t ai origins in the technological sense, but they represent the fertile ground from which the field would eventually grow. This period provided a rich backdrop of conceptual frameworks that would be later translated into tangible research and development.
The Dartmouth Workshop: A Turning Point
The true beginning of AI as a formal academic field can be traced to the Dartmouth Workshop in 1956. This two-month summer gathering, organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, brought together some of the brightest minds to explore what they called “artificial intelligence.” This is what is considered by many to be the start of the artificial intelligence timeline.
- The Proposal: The workshop’s proposal famously stated, “The study is to proceed on the basis of the conjecture that every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can in principle be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it.” This daring statement set the tone for the ambitious goals of early ai research.
- Key Participants: The participants, including luminaries like Allen Newell and Herbert Simon, were the pioneers of the field. Their contributions laid the groundwork for many of the AI approaches we see today.
- The Formal Birth: The Dartmouth Workshop is widely regarded as the official founding event of AI as a research discipline. It marked the transition from philosophical speculation to concrete technical pursuit.
The Dawn of Symbol Processing: Early AI Research Approaches
Following the Dartmouth workshop, the initial approach focused on symbol processing— manipulating symbols to represent knowledge and solve problems. Think of it like trying to explain things to a computer in a language it understands.
- Logic-Based AI: Researchers believed that logic could be used to represent knowledge and enable reasoning. This involved creating formal systems of logic and trying to get machines to follow the rules.
- Heuristics: Since logic wasn’t always practical for real-world problems, researchers started developing heuristics – rule-of-thumb strategies that offered reasonable, though not guaranteed, solutions. This was often described as a “good-enough” approach.
- Early Programs: Some of the first programs included:
- The Logic Theorist: Developed by Newell and Simon, this program could prove theorems in logic using human-like problem solving methods. It was one of the very first ai program demonstrations and a major landmark.
- ELIZA: Joseph Weizenbaum’s ELIZA program could engage in seemingly intelligent conversations by mimicking the patterns of a Rogerian psychotherapist. Although it did not ‘understand’ conversations, it gave the impression that it did.
- SHRDLU: Terry Winograd’s SHRDLU, another landmark program, understood natural language in a limited “blocks world” setting. It could answer questions and execute commands related to manipulating different colored blocks on a virtual tabletop.
These early ai research efforts were groundbreaking. They proved that computers could handle more than just number-crunching. They could manipulate symbols and mimic, however imperfectly, some aspects of human intelligence.
AI Milestones: A Look at the Key Developments
The artificial intelligence timeline is full of significant accomplishments that have shaped the field. Here’s a snapshot of some ai milestones:
| Time Period | Milestone | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950s-1960s | Early Symbolic AI Programs | Programs like Logic Theorist, ELIZA, and SHRDLU demonstrated basic problem-solving and natural language processing capabilities. | Showed the potential of AI beyond mere number crunching. Demonstrated problem solving using simple logical approaches. |
| 1970s | Expert Systems | Programs designed to emulate the decision-making abilities of human experts in specific domains (e.g., medical diagnosis). They used rules-based approaches. | Demonstrated practical applications of AI in specialized fields. Began to demonstrate expert system technologies. |
| 1980s | AI Winter & Revival | Funding and research stagnated due to limitations and over-promises. Later revival driven by progress in machine learning and neural networks. AI moved away from symbolic approaches and adopted a more probabilistic approach. | Highlighted the importance of managing expectations and demonstrated how machine learning could overcome limitations of older rule based systems. |
| 1990s | Machine Learning Breakthroughs | Emergence of powerful machine learning algorithms, including support vector machines (SVMs) and boosting algorithms. | Enabled AI systems to learn from data, rather than relying solely on explicit rules. Increased flexibility and usefulness. |
| 2000s-Present | Deep Learning Revolution | Deep neural networks, inspired by the structure of the brain, showed unprecedented capabilities in image recognition, speech processing, and other tasks. | Powered major advancements in areas like computer vision, natural language processing, and robotics. The current AI boom has been driven by these advancements. |
Major AI Breakthroughs: Pushing the Boundaries
Along with major milestones, certain major ai breakthroughs have redefined the field and opened up new possibilities. Here are some notable examples:
- Deep Blue beats Garry Kasparov (1997): This IBM computer defeating the world chess champion was a huge achievement, showcasing the power of computing and complex algorithms, even if it wasn’t truly “intelligent” in the human sense.
- ImageNet Challenge (2012): The deep learning models achieving dramatically better results in image recognition marked a shift toward modern deep learning architectures. AlexNet, the winning algorithm, demonstrated how deep neural networks could solve complex vision problems and sparked the current deep learning revolution.
- AlphaGo defeats Lee Sedol (2016): The Google DeepMind program mastered the complex game of Go, a game far more complex than chess. This demonstrated the ability of AI to surpass human abilities in strategic thinking.
- GPT-3 and Large Language Models: The emergence of sophisticated natural language models like GPT-3 have made it possible for machines to generate human-quality text, translate languages, and engage in meaningful conversations. It changed the way we look at natural language processing and highlighted the potential of transformer architectures.
These major ai breakthroughs have not only advanced the field but have also raised important questions about the future of AI.
AI Development Stages: A Path of Iteration
The ai development stages can be broadly divided into three main phases, though there is not a consensus on the names of the stages. It’s a journey of continuous improvement, each stage building on the knowledge and advancements of the previous one. Here’s how we can describe the broad ai development stages:
- Rule-Based AI (Early Days): This was the first stage, characterized by programs that relied on explicitly programmed rules to mimic intelligence. It was heavily dependent on humans to specify the reasoning process and logical steps. These approaches were limited because they could not generalize well to unexpected situations. Think of the classic if/then/else approach of programming.
- Machine Learning (The Data Era): As more data became available, machine learning became the dominant approach. These systems learn from the data without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning included a variety of approaches, including those using statistical methods to model probabilities, or those using neural networks with a couple of layers.
- Deep Learning (Neural Networks Take Center Stage): Deep learning builds on machine learning and uses neural networks with many layers to analyze complex patterns in massive datasets. Deep learning has revolutionized the field and is responsible for many of today’s most impressive AI applications. Modern day AI is heavily dependent on these complex neural network architectures.
The trajectory of AI has seen a clear shift from manually coded rules to data-driven learning. Based on extensive knowledge of the ai development stages, it’s evident that each phase has contributed significantly to the sophistication we see today. The journey continues with active research to improve these approaches and push the field even further.
Looking Ahead: What the Future Holds
The history of ai development is still being written. AI continues to evolve at a rapid pace and is being used in many aspects of our lives. As AI systems become more advanced, they raise some really important questions:
- Ethical Considerations: How do we ensure that AI systems are used responsibly and ethically? How do we prevent AI from being used in a way that could cause harm to individuals or society?
- Impact on Jobs: What will be the long-term effects of AI on employment? We need to understand how AI could displace workers and come up with effective methods to help those affected.
- The Future of Human-AI Interaction: How will we work with AI in the future? How can we create systems that collaborate effectively with humans, allowing us to harness the power of AI while retaining control?
While we may not have a simple answer to the question “When did AI start?”, we do know that the journey has been filled with extraordinary ideas and incredible technological advancements. Drawing from years of experience in the field, I’ve come to appreciate this dynamic evolution. The field continues to accelerate and shape our world in fundamental ways.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What was the very first AI program?
A: The Logic Theorist, developed by Newell and Simon, is often credited as one of the first AI programs. It could prove logical theorems using a symbolic approach.
Q: Who is considered the father of AI?
A: There is no single “father,” but John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon are considered the founders of AI because they organized the 1956 Dartmouth Workshop, which officially launched AI as an academic field.
Q: What is the difference between AI and machine learning?
A: AI is the broader concept of creating intelligent machines. Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on enabling computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
Q: Was AI invented by a single person?
A: No, AI development is the result of the work of many scientists, mathematicians, philosophers, and engineers. There is no single inventor.
Q: Is AI already smarter than humans?
A: In many specific tasks, AI can surpass human performance, particularly in computation and data processing. However, AI systems lack the general intelligence, consciousness, and emotional intelligence of humans.
Q: What is the AI Winter?
A: The term refers to a period in the 1970s and 1980s when AI research faced significant funding cuts and interest waned due to the limitations of the technology at the time.
Q: How has deep learning revolutionized AI?
A: Deep learning has revolutionized AI by using multi-layered neural networks to process vast amounts of data, enabling AI systems to achieve significant breakthroughs in areas like computer vision, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
I’m Rejaul Karim, an SEO and CRM expert with a passion for helping small businesses grow online. I specialize in boosting search engine rankings and streamlining customer relationship management to make your business run smoothly. Whether it's improving your online visibility or finding better ways to connect with your clients, I'm here to provide simple, effective solutions tailored to your needs. Let's take your business to the next level!

